Frontiers | Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus | Cellular and Infection Microbiology

In-Depth Characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus Phosphoproteome Reveals New Targets of Stk1 - ScienceDirect

Alteration of protein homeostasis mediates the interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Staphylococcus aureus.,Molecular Microbiology - X-MOL

Implications of identifying the recently defined members of the Staphylococcus aureus complex S. argenteus and S. schweitzeri: a position paper of members of the ESCMID Study Group for Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Diseases (
Nasal Colonisation by Staphylococcus aureus Depends upon Clumping Factor B Binding to the Squamous Epithelial Cell Envelope Protein Loricrin

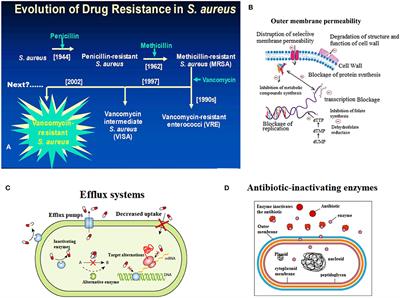
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an overview of basic and clinical research.,Nature Reviews Microbiology - X-MOL
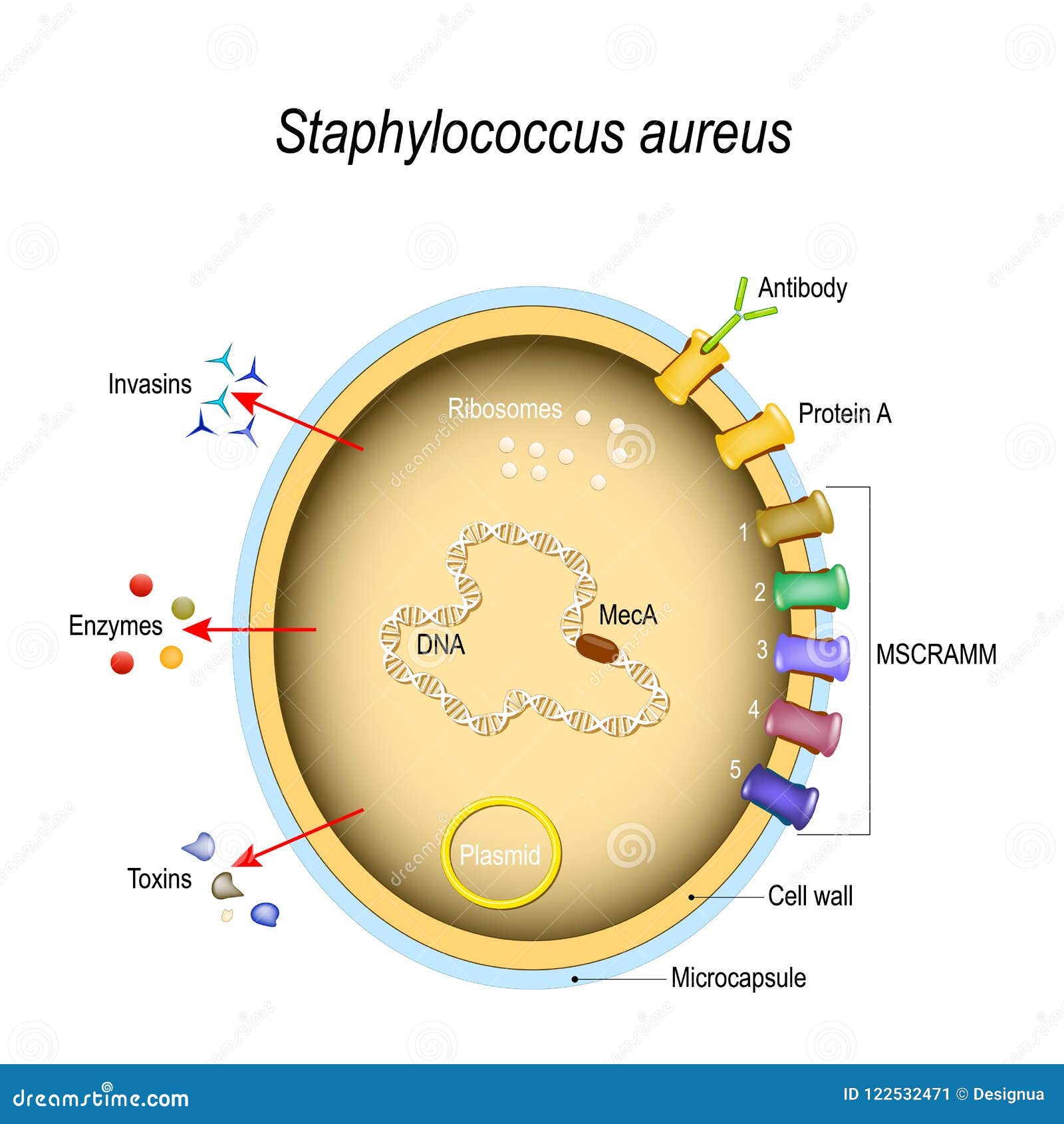
Staphylococcus Aureus Cell Structure and Pathogenic Factors Stock Vector - Illustration of epidemic, medical: 122532471

Impact of Staphylococcus aureus on Pathogenesis in Polymicrobial Infections | Infection and Immunity

Friends or enemies? The complicated relationship between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus,Molecular Microbiology - X-MOL

Structural basis for (p)ppGpp synthesis by the Staphylococcus aureus small alarmone synthetase RelP - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Strain Prevents Staphylococcus aureus Colonization and Skin Infection by Blocking Quorum Sensing - ScienceDirect
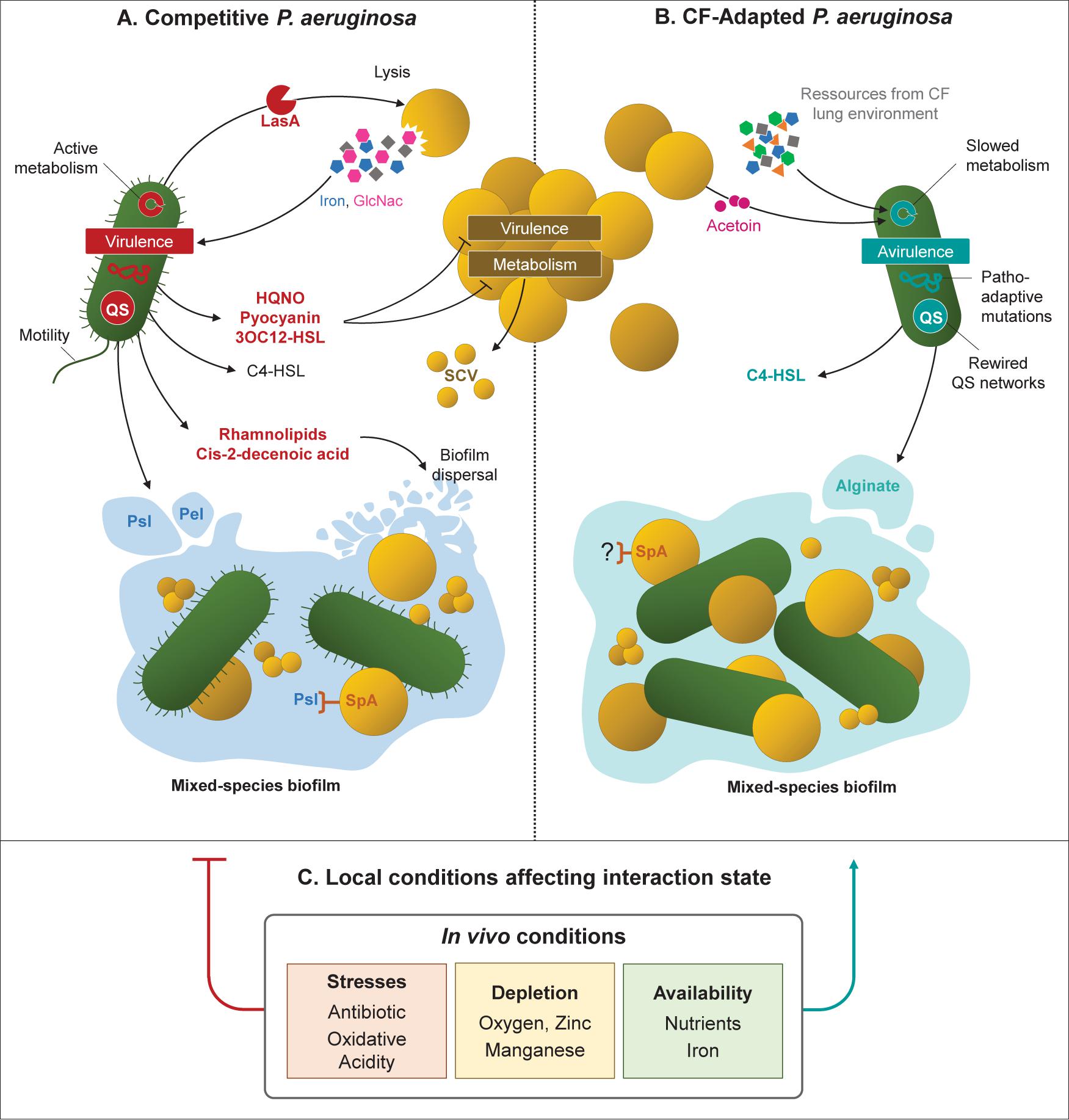
Frontiers | How Bacterial Adaptation to Cystic Fibrosis Environment Shapes Interactions Between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus | Microbiology

Coculture of Staphylococcus aureus with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Drives S. aureus towards Fermentative Metabolism and Reduced Viability in a Cystic Fibrosis Model | Journal of Bacteriology

Host nutrient milieu drives an essential role for aspartate biosynthesis during invasive Staphylococcus aureus infection | PNAS
PLOS ONE: Active Immunization with an Octa-Valent Staphylococcus aureus Antigen Mixture in Models of S. aureus Bacteremia and Skin Infection in Mice
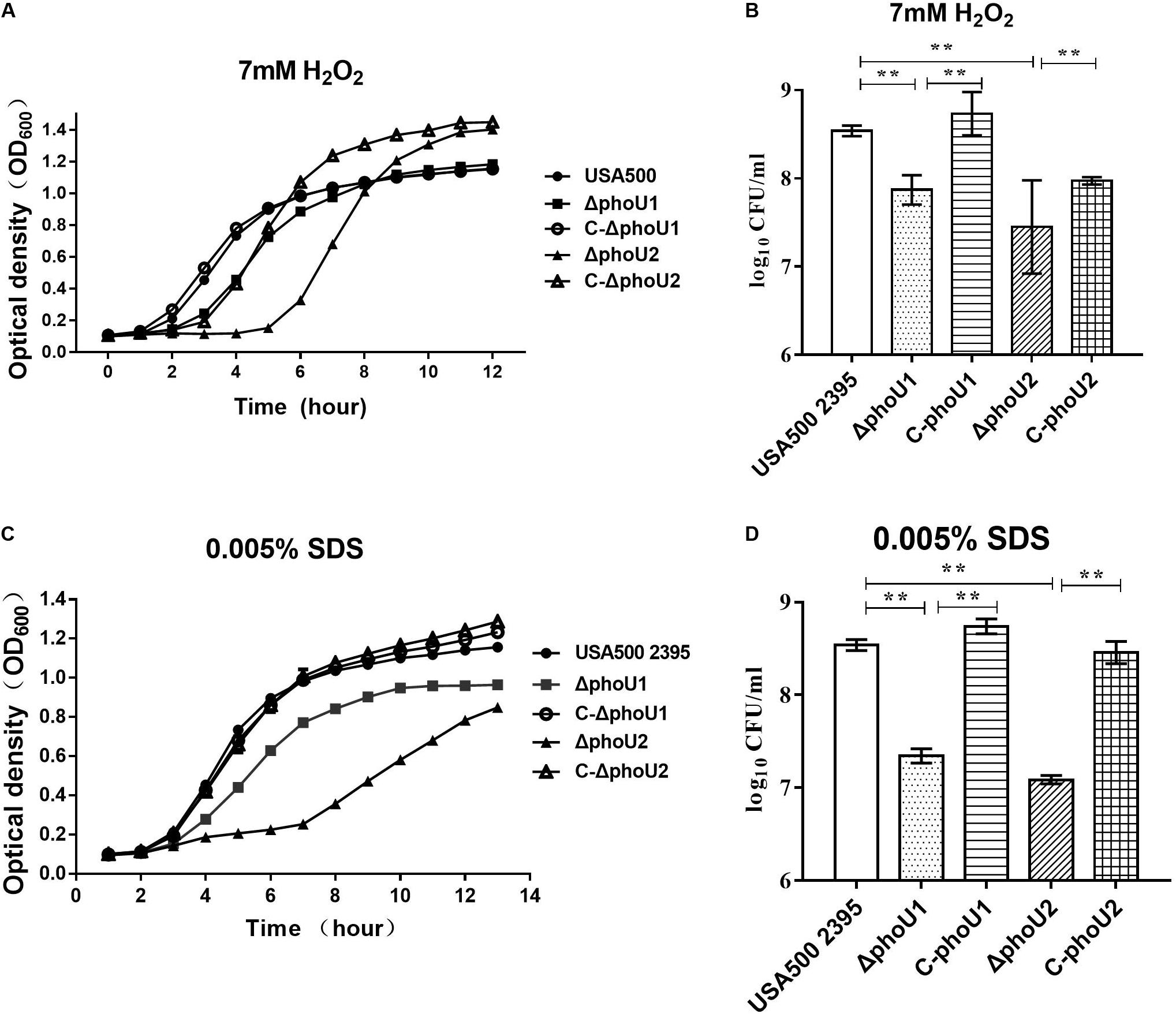
Frontiers | Staphylococcus aureus PhoU Homologs Regulate Persister Formation and Virulence | Microbiology

![PDF] Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa- Biofilm formation Methods | Semantic Scholar PDF] Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa- Biofilm formation Methods | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/89a1758dd5f7255689c06332201679487775107a/2-Table1-1.png)